What is the difference between the various veneers used for wood doors?
Thickness of veneer: 0.4mm-1mm regular veneer, commonly used as door surface veneer or sealing, less than 0.4mm thin veneer, often in the back of the non-woven fabric laminated, also known as non-woven veneer, commonly used to wrap the surface.
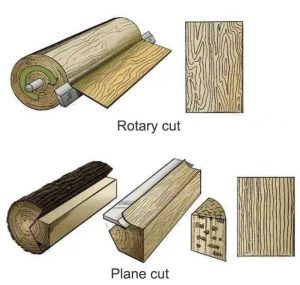
1. Natural Veneer
Natural veneer is taken from natural logs, and pasted on the substrate through the hot pressing process.
Advantages: natural texture and the fragrance of wood, veneer removed after high-temperature steaming before put to use, good veneer elasticity.
Disadvantages: low utilization, natural wood veneer is restricted, usually in the form of long strips that are not too wide, and need to be cut and spliced when used over a large area.

2. Smoked Veneer
Smoked veneer also known as carbonized veneer, natural wood veneer baked in high temperature, the moisture is further removed, so that the surface forms a thin carbonized layer, which can highlight the surface of the bumpy wood grain, producing a three-dimensional effect. It is more popular in retro style and industrial style.
Advantages: the texture is convex and concave with obvious effect, the grain is very clear, there is a retro style.
smoked wood veneer is very stable after baking, sunscreen, insect, moisture and durable.
Environmentally friendly and non-toxic: smoked wood veneer is baked at high temperature without the use of chemical reagents to reduce formaldehyde.
Disadvantages: relatively brittle, almost no moisture after high temperature baking, the veneer is very brittle, so the general smoked veneer is thicker.
Limited color choice, smoked veneer needs to be carbonized, so the color options are limited to dark colors.

3. Engineered Veneer
Engineered veneer is called restructuring veneer, generally use sycamore, poplar, paulownia, pine, eucalyptus, these fast-growing wood as a substrate. The use of a series of processing to achieve imitation of other species of wood grain. The process is: rotary cutting – dyeing – drying – restructuring – gluing – hot pressing – plane cutting.
Advantages: many colors, the pattern is designed to produce a variety of textures and colors, basically unlimited.
Wide range of applications, can make curved surfaces, shaped surfaces.
Price stability, there will be no major price fluctuations, a variety of price uniformity.
Disadvantages: shallow grain, thin veneer, after re-adaptation of the grain is not as deep as the real grain.
each producer manufacturing engineered wood veneer color and details are difficult to unify.

